Essential Scrum Roles & Responsibilities Explained Clearly
The Scrum framework is a cornerstone of Agile project management, offering a structured yet flexible approach to delivering high-quality products. Essential Scrum roles—Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team—each play a crucial part in driving project success. Misunderstanding these roles often leads to inefficient workflows, missed deadlines, and product misalignment with business goals.
Unlike traditional management approaches, Scrum empowers teams to self-organize, fosters transparency, and accelerates value delivery through iterative sprints. The Product Owner represents business interests and maximizes product value, while the Scrum Master acts as a servant leader who clears roadblocks and ensures adherence to Agile principles. Meanwhile, the Development Team delivers potentially shippable product increments each sprint.
This comprehensive guide demystifies these roles and their distinct responsibilities, offering a clear, actionable breakdown. Whether you're a project leader, developer, or stakeholder, this article will equip you with the deep, practical insights needed to leverage Scrum roles effectively. From role-specific tasks to real-world scenarios and certification insights, we’ll break down exactly what each Scrum role demands—ensuring your teams move faster, deliver better, and stay ahead of the competition.
The Three Scrum Roles
Scrum operates through three distinct roles, each with non-overlapping responsibilities critical to project success. This structure ensures clarity, accountability, and streamlined collaboration, leading to faster product delivery and higher stakeholder satisfaction.
Product Owner Responsibilities
The Product Owner serves as the voice of the customer, translating business goals into actionable backlog items. This role defines the product vision, prioritizes the Product Backlog, and ensures the Development Team is always working on the most valuable features. They collaborate closely with stakeholders to gather requirements, continuously refine backlog items, and accept or reject work results based on the Definition of Done. Product Owners must balance competing interests, make swift decisions, and ensure the backlog reflects the evolving market and customer needs. Success in this role demands strong communication, decision-making, and a deep understanding of both the product and user expectations.
Scrum Master Responsibilities
The Scrum Master acts as the Agile facilitator, ensuring that the Scrum framework is properly implemented. Their primary responsibility is to remove impediments that block the Development Team's progress and foster a culture of continuous improvement. They coach team members on Agile principles, facilitate Scrum ceremonies, and shield the team from external disruptions. Unlike traditional managers, Scrum Masters do not have authority over the team’s work. Instead, they serve as a bridge between stakeholders and the team, ensuring collaboration remains effective and efficient. Key competencies include servant leadership, conflict resolution, and a mastery of Scrum rules and best practices.
Development Team Responsibilities
The Development Team carries out the actual work of delivering product increments in each sprint. Comprising cross-functional professionals—developers, testers, designers—the team is self-organizing and collectively responsible for meeting sprint goals. They manage their own workload, estimate tasks, and ensure that deliverables meet the Definition of Done. The team collaborates daily through Scrum events like Daily Stand-ups and Sprint Planning, continuously adjusting plans to maximize value delivery. High-performing Development Teams demonstrate adaptability, technical excellence, and a commitment to team collaboration. Their focus remains squarely on delivering potentially shippable increments, sprint after sprint, in line with the Product Owner’s vision.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Product Owner | Serves as the voice of the customer, translating business goals into actionable backlog items. Defines the product vision, prioritizes the Product Backlog, and ensures the Development Team works on the most valuable features. Collaborates with stakeholders to gather requirements, refines backlog items, and accepts or rejects work results based on the Definition of Done. Balances competing interests, makes swift decisions, and ensures the backlog reflects evolving market needs. |
| Scrum Master | Acts as the Agile facilitator, ensuring Scrum framework implementation. Removes impediments blocking the Development Team’s progress, fosters a culture of continuous improvement, and coaches on Agile principles. Facilitates Scrum ceremonies and shields the team from external disruptions. Serves as a bridge between stakeholders and the team. Key competencies include servant leadership, conflict resolution, and mastery of Scrum rules and best practices. |
| Development Team | Executes the actual work of delivering product increments in each sprint. Comprises cross-functional professionals (developers, testers, designers) and is self-organizing. Manages workload, estimates tasks, and ensures deliverables meet the Definition of Done. Collaborates daily through Scrum events like Daily Stand-ups and Sprint Planning. Demonstrates adaptability, technical excellence, and commitment to team collaboration, delivering potentially shippable increments aligned with the Product Owner’s vision. |
Key Responsibilities Across Scrum Roles
Scrum roles intertwine through shared responsibilities that drive projects toward successful outcomes. The structured approach of Scrum not only defines individual roles but also fosters synergy in planning, execution, and continuous improvement.
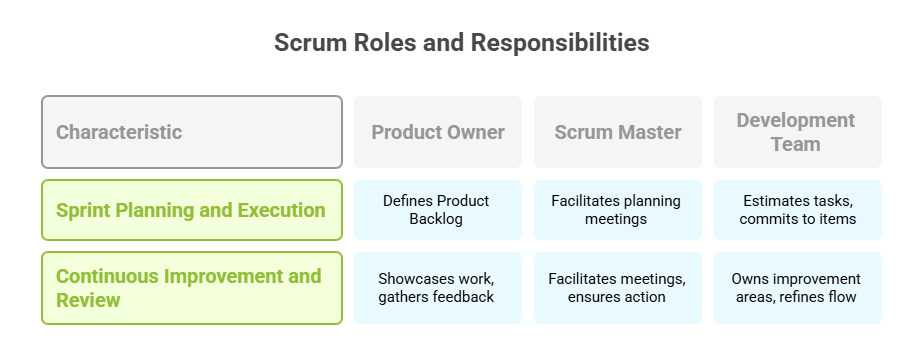
Planning and Sprint Execution
Every Scrum role contributes to Sprint Planning and execution. The Product Owner defines the Product Backlog, ensuring high-priority items are clearly described and ordered. They articulate the Sprint Goal, providing clarity on what the team must deliver to create value. The Scrum Master facilitates the planning meeting, ensuring a structured approach and resolving any blockers early. Meanwhile, the Development Team estimates tasks, determines the sprint’s workload capacity, and commits to delivering specific backlog items. Throughout the sprint, the team maintains a Daily Scrum—a short meeting to synchronize efforts and identify impediments.
Execution relies on close alignment with the Sprint Goal. The Development Team manages task ownership, collaborates on solutions, and ensures that each deliverable adheres to the Definition of Done. The Scrum Master monitors progress, resolves external disruptions, and reinforces Agile practices, while the Product Owner stays engaged, ready to refine backlog items as needed. This dynamic interplay ensures that the sprint remains on track, focused, and valuable.
Continuous Improvement and Review
The Scrum framework emphasizes continuous learning and process refinement. After each sprint, all roles engage in the Sprint Review and Sprint Retrospective. The Product Owner showcases completed work to stakeholders during the Sprint Review, gathering feedback to adjust the Product Backlog. The Scrum Master facilitates both meetings, ensuring that feedback is actionable and that team dynamics are constructively addressed. They help surface underlying issues that may affect future sprints, promoting an environment of psychological safety where open dialogue is encouraged.
The Development Team takes ownership of improvement areas identified during retrospectives, implementing adjustments in future sprints. Whether it’s refining estimation practices, improving task flow, or adopting new tools, the team’s agility enhances with every iteration. By fostering a culture of inspection and adaptation, Scrum enables teams to elevate their performance, deliver higher-quality products, and stay aligned with business goals.
Real-World Examples of Scrum Role Execution
Understanding Scrum roles is enhanced by real-world scenarios showcasing their interaction and impact. Let’s explore two distinct examples that illuminate how these roles play out under practical constraints and opportunities.
Scenario 1: Agile Product Development
A mid-sized SaaS company initiates a new product feature requiring rapid delivery. The Product Owner collaborates with stakeholders to define a detailed backlog, incorporating market research and customer feedback. They prioritize high-value items, ensuring the sprint goal aligns with business objectives. During Sprint Planning, the Scrum Master guides the team through workload estimation, addressing potential impediments such as resource limitations or technical debt. The Development Team commits to delivering the most critical backlog items, balancing functionality with maintainability.
Throughout the sprint, the Scrum Master shields the team from distractions, facilitates daily stand-ups, and encourages adherence to Agile principles. The Product Owner remains available for clarifications and backlog adjustments. The sprint concludes with a Sprint Review, where the team showcases the completed feature, gathering valuable stakeholder input. A Sprint Retrospective follows, surfacing actionable insights on improving delivery speed and technical quality. This scenario underscores the essential, role-specific contributions to fast, efficient product development.
Scenario 2: Scaling Scrum in Enterprises
A multinational enterprise adopts Scrum to coordinate multiple teams working on an integrated solution. Each Product Owner manages a distinct backlog aligned with a shared product vision. Scrum Masters synchronize ceremonies across teams, ensuring impediments are swiftly resolved and best practices consistently applied. The Development Teams focus on delivering individual increments while collaborating with other teams to ensure seamless integration.
During Sprint Planning, cross-team dependencies are identified and managed proactively. The Scrum Masters facilitate communication, resolving conflicts and aligning sprint goals. The Product Owners participate in backlog refinement sessions to balance local priorities with overarching business needs. Regular Sprint Reviews involve senior stakeholders, while combined Retrospectives identify process inefficiencies and cross-team improvement opportunities. This example highlights Scrum’s scalability and the pivotal role of each actor in delivering complex, high-stakes projects with agility and precision.
| Poll: What aspect of Scrum do you find most valuable? | |
|---|---|
| Clear roles and responsibilities | |
| Continuous improvement and feedback | |
| Agile adaptability and team collaboration | |
How Our Project Management Certification Equips You for These Scrum Roles
The journey to mastering Scrum begins with comprehensive, role-based training. Our Project Management Certification goes beyond theoretical frameworks, delivering practical expertise and the skills needed to thrive in dynamic Agile environments.
Role-Based Training Highlights
Our program is meticulously designed to cover the core competencies and advanced techniques of the Scrum Master role. Participants gain in-depth knowledge of Scrum principles, Agile methodologies, and proven strategies for facilitating high-performing teams. Hands-on simulations replicate real-world challenges, training participants to manage impediments, foster team collaboration, and drive continuous improvement.
The curriculum also covers Agile coaching techniques, conflict resolution, and stakeholder engagement strategies, equipping Scrum Masters to navigate complex organizational landscapes. Learners develop expertise in key ceremonies—Sprint Planning, Reviews, and Retrospectives—ensuring they can maintain process integrity while maximizing value delivery.
Throughout the program, learners apply their knowledge to case studies and role-playing exercises, reinforcing practical skills. By the end, participants can confidently implement Scrum principles, lead Agile transformations, and drive business outcomes. The emphasis is not just on theory, but on actionable skills that translate into measurable improvements in team productivity and delivery quality.
Advanced Project Management Certification by APMIC
For those ready to elevate their skills and impact, our Advanced Project Management Certification offers a comprehensive learning pathway, CPD-accredited and PMI-aligned, delivering 542 expert-level lessons and covering 80+ industry tracks. Designed for college graduates, early-career project managers, and career changers, the program requires no prior project management experience.
Explore full program details and enrollment options here. The curriculum spans Agile, Waterfall, Scrum, Kanban, SAFe, and Hybrid methodologies, providing in-depth training in risk management, scope definition, cost control, leadership, earned value management (EVM), project tools, and governance.
Conclusion
The Scrum framework transforms project delivery by defining clear roles and responsibilities, aligning teams, and driving continuous improvement. Whether it’s the Product Owner, Scrum Master, or Development Team, each role contributes distinct yet complementary value to ensure sprint goals are met and stakeholder needs are exceeded.
Through focused backlog management, proactive facilitation, and hands-on product development, Scrum roles create a synergistic environment where projects progress smoothly, with minimal friction and maximum adaptability. This clarity of responsibilities fosters faster delivery, higher-quality outcomes, and a culture of innovation that sets Agile organizations apart from traditional project management approaches.
Our Project Management Certification program is tailored to equip you with the skills, insights, and techniques to excel in any Agile environment. It offers comprehensive, real-world training designed to make you not just a participant in Scrum, but a catalyst for Agile transformation.
Take the next step towards becoming a recognized leader in Agile delivery. Empower your teams, accelerate delivery, and drive business success by embracing the distinct yet interconnected roles that make Scrum a powerful project management framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
The Product Owner focuses on maximizing product value by managing the backlog and aligning with stakeholder needs. The Scrum Master facilitates the Scrum framework, clears impediments, and fosters Agile principles within the team. The Development Team is self-organizing and responsible for delivering the product increment. Each role has distinct responsibilities, ensuring clarity and efficiency. The Product Owner sets priorities, the Scrum Master enables productivity, and the Development Team builds the product. This clear separation drives faster delivery, stakeholder satisfaction, and continuous improvement in Agile projects.
-
Our Project Management Certification provides comprehensive training in Agile methodologies, including Scrum, Kanban, and SAFe. It equips you with essential skills to lead Agile transformations, manage team dynamics, and drive process improvements. The certification is CPD-accredited and PMI-aligned, offering 542 lessons across 80+ industry tracks, ideal for career changers and early-career professionals. You’ll gain practical expertise in Agile practices, leadership, conflict resolution, and stakeholder engagement, enhancing your credibility and employability. This credential is highly recognized, opening doors to senior roles in project management and Agile coaching.
-
Absolutely. Our Project Management Certification is designed for college graduates, early-career professionals, and career changers with no prior project management background. The curriculum covers foundational to advanced Agile concepts, equipping learners with the knowledge, skills, and practical experience required to excel in Scrum roles. Participants gain hands-on exposure to real-world scenarios, learn facilitation techniques, and develop confidence in managing Scrum ceremonies. This approach ensures even those new to project management can master Agile delivery, gain credibility, and transition seamlessly into a Scrum Master role.
-
The Scrum Master ensures that the team follows Agile principles and Scrum guidelines during sprint execution. They facilitate daily stand-ups, remove impediments, and protect the team from external distractions. The Scrum Master also coaches the team on self-organization, encourages cross-functional collaboration, and ensures adherence to the sprint goal. By maintaining process integrity and addressing issues proactively, the Scrum Master maximizes productivity and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. This role is pivotal in delivering high-quality product increments efficiently.
-
Scrum scales effectively through frameworks like Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) or Large Scale Scrum (LeSS). In enterprise settings, multiple Product Owners manage specific backlogs aligned with the overall product vision. Scrum Masters synchronize cross-team ceremonies, manage dependencies, and resolve conflicts. Development Teams focus on delivering their increments while collaborating for integration. Regular combined retrospectives identify inefficiencies and drive improvements. Scaled Scrum enables large organizations to maintain agility, promote collaboration, and deliver integrated solutions efficiently, without sacrificing the core values of Scrum.
-
Scrum ceremonies follow a set cadence: Sprint Planning occurs at the beginning of each sprint, aligning goals and workloads. Daily Stand-ups (or Daily Scrum) are held every day to synchronize efforts. Sprint Review is conducted at the end of the sprint to showcase deliverables to stakeholders. Sprint Retrospective follows the review, focusing on team performance and identifying improvements. This structured rhythm ensures continuous inspection, adaptation, and progress tracking. Maintaining this cadence is vital for sustaining Scrum’s effectiveness and delivering valuable increments consistently.
-
A successful Scrum Master combines technical knowledge of Scrum and Agile with strong facilitation, coaching, and leadership skills. They must possess excellent communication to engage stakeholders and foster collaboration, adept problem-solving to remove impediments, and a deep understanding of Scrum principles to guide the team. Emotional intelligence, adaptability, and conflict resolution abilities are crucial. The Scrum Master serves as a servant leader, focusing on enabling the team’s success while maintaining Agile integrity and continuous improvement.